Understanding Blood Pressure by Age: What You Need to Know
According to the U.S. CDC, an estimated 48.1% of U.S. adults, or 119.9 million people, have high blood pressure, also known as hypertension.
Hypertension occurs when a person has higher than normal blood pressure levels. It usually develops over time and with age, which is why it's more common among seniors.
So, if you or a loved one is getting in on years, it's crucial to learn about the optimal blood pressure goal for elderly individuals. There's no cure for hypertension, only treatment, but it's possible to maintain a healthy blood pressure range without medication.
To that end, our team at Lehigh Acres Assisted Living in Lehigh Acres, FL, put together this guide on blood pressure. Read on to discover age-specific blood pressure recommendations and tips for monitoring and controlling yours.
Understanding Blood Pressure Numbers
Blood pressure (BP) readings consist of two numbers. The top or first number, called systolic pressure, measures the pressure in the arteries during a heartbeat. The second or bottom number, diastolic pressure, gauges the pressure in the arteries between each heartbeat.
The standard unit of measure used for BP readings is millimeters of mercury, abbreviated as "mm Hg." Electronic pressure gauges have replaced the mercury ones, but the abbreviation remains.
Recommended Blood Pressure Levels by Age
The following are the ideal blood pressure levels (systolic and diastolic, respectively), according to Baptist Health's blood pressure chart by age:
- Newborns to 1 month old: 60 to 90 mm Hg / 20 to 60 mm Hg
- Infants: 87 to 105 mm Hg / 53 to 66 mm Hg
- Toddlers: 95 to 105 mm Hg / 53 to 66 mm Hg
- Preschoolers: 95 to 110 mm Hg / 56 to 70 mm Hg
- School-aged children: 97 to 112 mm Hg / 57 to 71 mm Hg
- Adolescents: 112 to 128 mm Hg / 66 to 80 mm Hg
- Adults: Under 120/80 mm Hg
Doctors may diagnose adults whose blood pressure levels consistently exceed 120/80 mm Hg with hypertension.
Categories of Blood Pressure Levels in Adults
Blood pressure levels in adults also have categories. Pay attention to your numbers: Even a one-digit increase in systolic or diastolic levels can already put you in the group with hypertension.
- Normal: Under 120/80 mm Hg
- Elevated: Between 120 and 129 mm Hg / Under 80 mm Hg
- Stage 1 high blood pressure: Between 130 and 139 / between 80 and 89 mm Hg
- Stage 2 high blood pressure: 140 and higher / 90 or higher
- Hypertensive Crisis: Higher than 180 mm Hg / higher than 120 mm Hg
We hope you never get a reading that indicates a hypertensive crisis because it may put you at risk of severe problems like stroke and heart attack, per the American Heart Association (AHA). If you do, the AHA recommends taking another reading after one to two minutes. If the second reading is just as or even higher, and you also experience the following, please call 911 immediately:
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- Vision changes
- Difficulty speaking
- Confusion
- Numbness or weakness
- Vomiting and dizziness
If you don't experience those symptoms, you may not need hospitalization, but you may still be going through hypertensive urgency. Please have someone take you to the doctor as soon as possible.
Targets for Adults With Existing Hypertension
According to Guideline Central, several blood pressure guidelines for adults with hypertension exist. The most recent ones (for U.S. adults) include the following:
- 2022 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA)
- 2017 American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP)
The 2022 ACC/AHA guideline recommends that adults 18 and older (80+) with hypertension maintain a blood pressure level of under 140/90. The 2017 AAFP guideline recommends keeping BP levels under 130/90.
Tips for Reaching Blood Pressure Goal for Elderly Individuals
Hypertension is preventable. However, if your doctor has diagnosed you with this condition, you can take many steps, including lifestyle modifications, to control it. Here are some tips and strategies to help you achieve your optimal blood pressure goals.
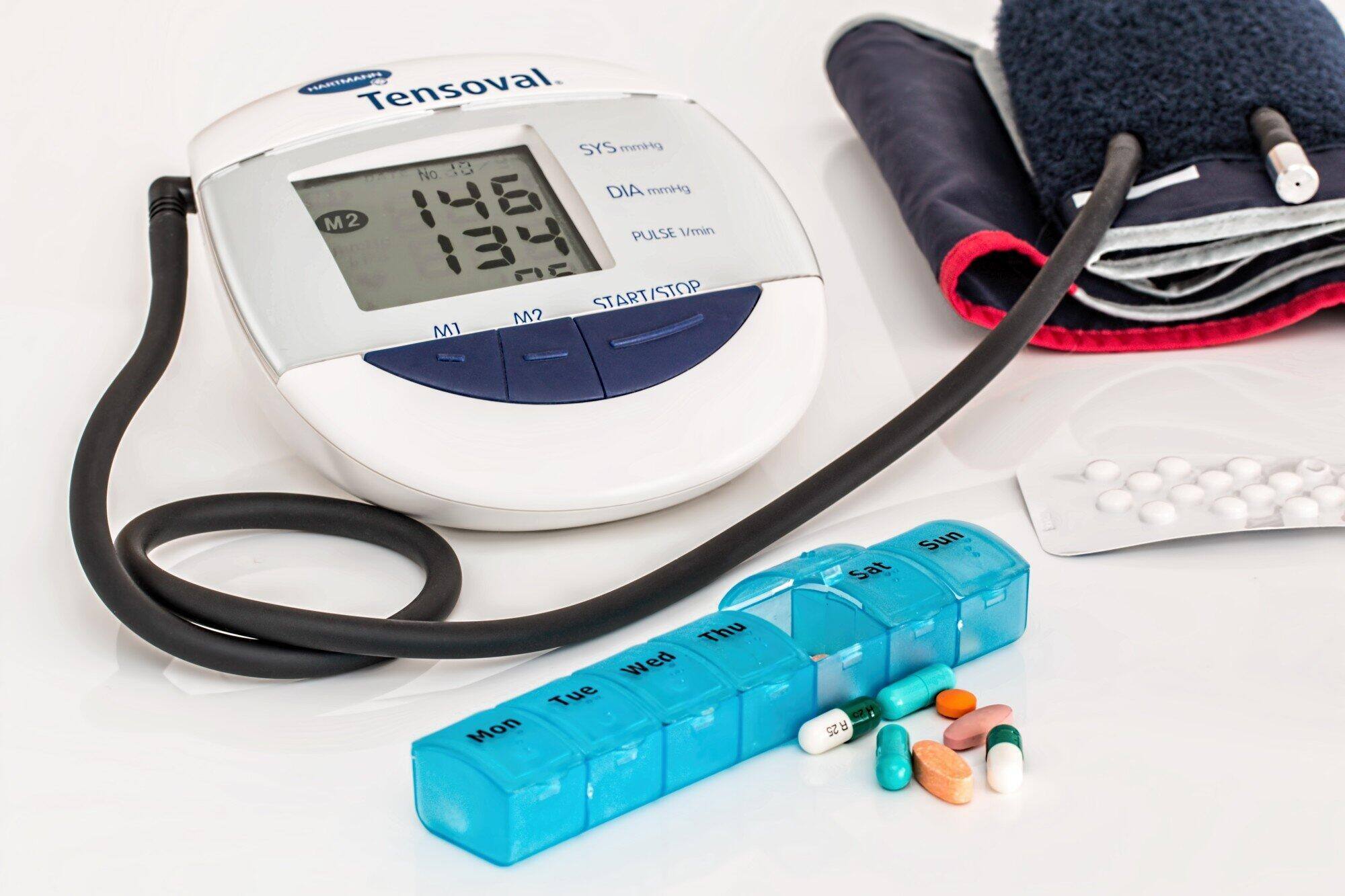
Invest in a Blood Pressure Monitor
With a personal or at-home blood pressure monitor, you can track your BP levels and determine whether you have hypertension or are maintaining a healthy range. The experts at Harvard Health recommend taking two readings in the morning and then two more at night for seven consecutive days. You can then average them to see where your blood pressure stands.
If your doctor has given you specific recommendations about monitoring your BP levels, follow their advice.
Blood Pressure Monitoring Tips
Take readings in a peaceful, stress-free environment. If there's too much going on around you or it's noisy, you may feel stressed, which can cause a spike in your BP levels.
Sit in a comfy chair with back support. Uncross your legs, and ensure the soles of your feet lie flat on the floor.
Roll the sleeves of your shirt up or change into a sleeveless top. Wrap your BP monitor's cuff around the upper part of a bare arm. The cuff should be in direct contact with the skin and snug enough that only one fingertip can go under.
Put your arm on a supportive surface, such as a tabletop. The cuff's center should be level with your heart. Once you're all set, you can turn the monitor on and record its reading.
Be More Physically Active
Physical activity can help control your blood pressure and weight. You can make it more fun by exercising with friends and choosing senior-friendly outdoor activities.
Eat Healthily
Natural low-fat foods, such as vegetables, fruits, and grains, are healthy for the heart and blood pressure. Your doctor may also recommend the low-salt Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet. Aside from being low in salt, DASH foods are high in calcium, magnesium, potassium, and fiber.
Take Medications as Prescribed
If your doctor prescribes medicines to help you control your blood pressure, please practice proper medication management. It involves taking the right medications, quantity, and dosage on time. The goal is to ensure your medicines work as they should while minimizing adverse drug event (ADE) risks.
Maintain Optimal Blood Pressure Levels
Achieving the optimal blood pressure goal for elderly individuals can help seniors live healthier. Proper monitoring, lifestyle changes, and correct medication management can all help keep BP levels under control.
At Lehigh Acres Assisted Living, we aim to help our residents live their lives to the fullest. We provide personal care services (including medication management) and senior-centered health and wellness activities. We're a vibrant, pet-friendly senior living community near downtown Fort Myers.
Schedule your visit today to learn more about how we can help you or your loved one enjoy your golden years!
